Many individuals aspire to attain a youthful, firm, and radiant complexion. However, as time passes, the skin inevitably experiences a decline in firmness, elasticity, and suppleness. This decline is often influenced by various factors such as prolonged sun exposure, genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices , and a reduction in collagen levels.
As a result, wrinkles , fine lines, and sagging skin become noticeable. To fight the adverse effects of these factors, a growing number of individuals are seeking out professional approaches to address these skin concerns.
There are various ways to address skin concerns, such as sagging or wrinkles, each offering different approaches and results. Most of the approaches follow non-invasive procedures or invasive procedures.
Non-invasive skin tightening methods use advanced technologies and natural processes to improve skin elasticity without surgery or prolonged recovery. Microcurrent therapy, in particular, has gained attention for its rejuvenating effects. In this article, we'll delve into the science behind microcurrent therapy and the importance of optimizing microcurrent frequency for effective skin tightening.
Understanding Microcurrent therapy
Microcurrent therapy is based on the body's natural bioelectric currents, which play a vital role in various biological processes, including tissue healing and regeneration. By replicating and amplifying these inherent electrical signals, microcurrent therapy aims to expedite the healing and rejuvenation of tissues.

The fundamental goal of this therapy is to promote tissue regeneration and rejuvenation, leading to improvements in skin tightening, elasticity, and overall youthfulness. It entails applying low-level electrical impulses, typically ranging from 0.1 to 1000 microamperes, to the skin. Through precise application, microcurrents can activate specific cells and tissues, triggering various physiological reactions that foster skin regeneration.
Microcurrent therapy for skin tightening
Within the intricate network of the human body, electrical impulses play a vital role in coordinating and transmitting communication between different parts of the organism. Microcurrent therapy utilizes low-level electrical impulses to stimulate cellular activity in the skin and underlying tissues.

The primary cause of sagging and wrinkles in the skin is the loss of muscle tone and elasticity. Employ a microcurrent device and perform targeted skin tightening exercises to help restore muscle tone and firmness. Understanding the mechanism of microcurrent therapy is essential to comprehend how it effectively tightens the skin.
Scientific evidence to prove the working of microcurrent therapy
A study was conducted to examine the effect of microcurrent therapy on treating facial wrinkles. This trial was conducted on thirty women with wrinkles but no other skin problems. All the women were less than 45 years of age. Their faces were treated with microcurrents for twenty minutes for thirty consecutive sessions.
After the results were gathered, 18.37% were with best forehead results. 21.18% belonged to women with the best nose and mouth area. The recovery proved better for the frontal wrinkles than the nose and mouth. The microcurrent therapy gave a 70% satisfaction rate among the patients.
Benefits of microcurrent therapy
Microcurrent therapy stimulates cellular-level developments, leading to several beneficial effects:
ATP Production
ATP, Adenosine Triphosphate, is the fundamental source of cellular energy, and microcurrent therapy increases its production. This boost in ATP allows cells to function optimally, facilitating necessary repairs within the body.
Collagen Production
Microcurrent therapy stimulates fibroblasts to produce collagen, a crucial protein providing structural support to the skin. Collagen helps maintain skin firmness and elasticity, contributing to a more youthful appearance.
Elastin Production
Another essential protein for skin elasticity is elastin. Microcurrent therapy prompts fibroblasts to produce elastin, further enhancing the skin's ability to stretch and restore its youthful appearance.
Improved Circulation
Microcurrent therapy enhances blood circulation in the treated skin area, leading to improved oxygenation, nutrient delivery, tissue healing, cell growth, and rejuvenation. This contributes to healthier skin and other skin benefits.
Choose an optimized microcurrent frequency
Choosing the appropriate microcurrent frequency is crucial for the effective implementation of microcurrent therapy. The frequency of the applied current directly influences the therapy's outcomes. Frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), denotes the number of oscillations per second. Various frequencies lead to distinct biological responses, making it essential to select the right frequency to achieve specific therapeutic results. Microcurrent therapy utilizes different frequencies for specific skin benefits:
Low frequencies
Low frequencies (0.1 Hz to 100 Hz) promote cellular repair and skin healing, stimulating ATP production, ion exchange, tissue repair, protein synthesis, and tissue regeneration. They are effective for treating skin lines, wrinkles, and scars due to increased collagen and elastin production.
Mid-range frequencies
Mid-range frequencies (100 Hz to 1000 Hz) improve blood circulation, lymphatic drainage, and reduce inflammation and redness in treated skin areas, enhancing overall cellular health.
High frequencies
High frequencies (over 1000 Hz) are mainly used for muscle stimulation, contributing to toning and firming facial muscles. However, they are not commonly preferred for skin tightening procedures.
To achieve accurate skin tightening results with microcurrent therapy, it is essential to select the frequency that matches the desired cellular response. Frequencies promoting collagen and elastin production, ATP production, and protein synthesis are generally favored. However, other factors, such as skin condition, age, and treatment goals, should also be considered when determining the ideal frequency range for each patient.
The treatment procedure
There are two ways to conduct microcurrent therapy procedures. It can be conducted in a clinical setting with a licensed esthetician. The practitioner examines the skin and determines the best suited treatment course based on the patient's skin history, skincare routine, and medical conditions. They customize the therapy, including selecting the suitable microcurrent frequency.

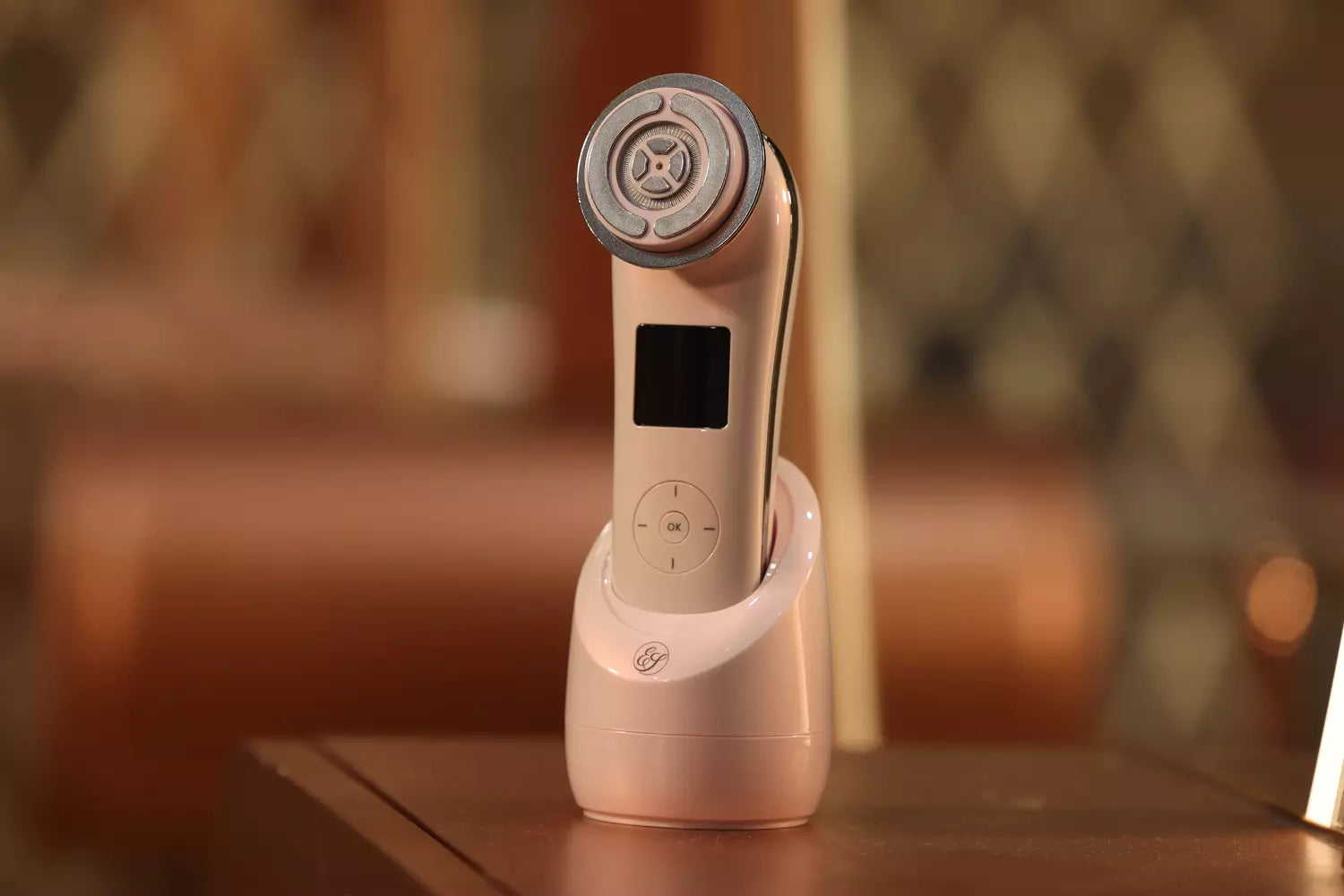
Alternatively, individuals can opt for at-home microcurrent therapy using clinically approved devices like the Evenskyn Phoenix: Premium Face Lifting Microcurrent Bar. This device utilizes natural and artificial light to generate a regulated microcurrent, lifting and recharging specific areas of the skin. For favorable results, it is recommended to use the device for five to ten minutes once within a twenty-four hour period.
Safety measures to follow
Microcurrent therapy is safe and straightforward when performed correctly. Following safety measures is crucial for optimal results. Microcurrent devices are non-invasive, requiring no surgery or incisions for skin tightening.
Some individuals may prefer traditional approaches over modern appliances, but using a microcurrent therapy device reduces the risk of side effects and prolonged recovery times compared to invasive methods.
Carefully reading and adhering to all provided guidelines, in addition to the manual instructions, is essential. Avoid using any microcurrent frequency device during pregnancy, epilepsy, or if you have an implanted electronic device. Being aware of and complying with these precautions enhances the safety and effectiveness of microcurrent therapy.
Maintenance measures for the device
Put the device in a dry, cool place when not in use. After each use, clean the device with a soft cloth to prevent scratches. Avoid using any metal polishing cloth on the Phoenix device.
Conclusion
Now that you know the optimal frequency range for skin tightening microcurrent therapy, you can confidently purchase the device and take charge of your beautiful skin. No need to worry about aging, as the solution is readily available.
This device offers a unique wrinkle-fighting experience with its science-backed performance and user-friendly design. The best part is that you can use the microcurrent therapy device anytime and anywhere.
References
Cao, Changwei et al. “Diet and Skin Aging-From the Perspective of Food Nutrition.” Nutrients vol. 12,3 870. 24 Mar. 2020.
Reilly DM, Lozano J. Skin collagen through the lifestages: importance for skin health and beauty. Plast Aesthet Res 2021.
Manríquez, Juan Jorge et al. “Wrinkles.” BMJ clinical evidence vol. 2014 1711. 22 Dec. 2014.
Saniee, Fatemeh & Khademi, Khosro & Yazdanpanah, Parviz & Rezasoltani, Asghar & Dabiri, Nader & Ghafarian Shirazi, Hamid Reza. (2012). The effect of microcurrents on facial wrinkles. Pars of Jahrom University of Medical Sciences.
Xu X, Zhang H, Yan Y, Wang J, Guo L. Effects of electrical stimulation on skin surface. Acta Mech Sin. 2021
Xu X, Zhang H, Yan Y, Wang J, Guo L. Effects of electrical stimulation on skin surface. Acta Mech Sin. 2021.
Kolimechkov, S., Seijo, M., Swaine, I. et al. Physiological effects of microcurrent and its application for maximising acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. 2023.
Saniee, Fatemeh & Reza, Hamid & Ghafarian Shirazi, Hamid Reza & Khademi, Khosro & Yazdanpanah, Parviz & Soltani, & Dabiri, Nader & Ghafaryan Shirazi, Nazanin & Karimpour, Farzad & Ghafarian, Fatima & Khademi, Shirazi & Yazdanpanah, Kalantari & Soltani, Pooyan. (2012).
Bolke, Liane et al. “A Collagen Supplement Improves Skin Hydration, Elasticity, Roughness, and Density: Results of a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Blind Study.” 17 Oct. 2019
Wunsch, Alexander, and Karsten Matuschka. “A controlled trial to determine the efficacy of red and near-infrared light treatment in patient satisfaction, reduction of fine lines, wrinkles, skin roughness, and intradermal collagen density increase.” Photomedicine and laser surgery vol. 32,2 (2014).
“Update on tissue tightening.” The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology vol. 3,5 (2010)
Gold, Michael H. “Noninvasive Skin Tightening Treatment.” The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology vol. 8,6 (2015)









Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.