Skin inflammation can occur due to various reasons and may look different for everyone. Some may develop a rash or redness due to external and internal factors. Factors such as allergies, infections, genetics and environmental exposure may trigger this inflammatory response.
The skin has a healing response to inflammation to repair and regenerate the dermis. It uses the network of cellular messengers known as cytokines to start the healing process.
This article explores the relationship between skin inflammation and cytokines, explaining the mechanisms that drive skin cell repair and regeneration. Keep reading to learn how non-invasive therapy, known as Red Light Therapy (RLT), can be used to modulate cytokines and promote skin healing.
What Causes Inflammation in the Skin?
Several factors may cause skin inflammation. Moreover, they may also vary on an individual skin type.

Allergies
Allergic reactions to substances like certain skincare products, cosmetics, fragrances, or even specific foods can lead to skin inflammation. This is often referred to as contact dermatitis. If you're using a new skin ingredient, it may cause redness, hives, and acne.
Infections
Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections can cause skin inflammation. Common examples include bacterial cellulitis, fungal infections like athlete's foot, or viral infections. Some people with autoimmune diseases, like dermatitis, psoriasis, and eczema, may be more susceptible to more infections in general.
Genetics may play a role in causing inflammation. Conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or scleroderma involve the immune system attacking healthy skin cells, leading to inflammation.
Photosensitivity
Sun's UV rays cause photoreaction in all skin types; however, some people may be more likely to develop a rash or inflammation. This sensitivity to the sun is known as photosensitivity.
Heat exposure
Prolonged exposure to heat, such as sunburn or contact with hot objects, can cause skin inflammation and redness. Any sudden change in temperature may have an impact on skin health.
Cytokines for Skin Repair and Healing
Our skin has several functions in place to constantly heal it. Right from the moment of inflammation or impact, the intricate process of healing starts. Neutrophils reach the inflammation site on the endothelium.
They help in tissue debridement and infection control. Besides, they generate a variety of growth factors for cell development and remove and degrade the extracellular matrix, making them involved in the wound healing process.
After this, the proliferative stage begins, where anti-inflammatory phenotypes are activated for wound healing. M1 Macrophages release pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-8 (IL-8). Macrophages are necessary for all the stages of wound healing, such as proliferation and remodeling.
Moreover, signaling molecules and cytokines aid in the shift from M1 to M2 phenotype. Most of these cytokines are produced by the immune cells, like regulatory T cells and Th2 lymphocytes. This is where transcription factors regulate gene expression and macrophage polarization.
In simple words, cytokines deliver the important messages between cells and tissues for repairs. Only through these messages, the cells are able to proliferate, repair and regenerate at the inflammation site. Also called immunomodulators, cytokines are the small proteins secreted by the immune system.
How do Cytokines Help the Skin Barrier
The skin barrier is crucial for skin health as it protects the skin from harmful factors and water loss. Keratinocytes create a complex skin barrier by morphing their integral structure. Via the process of cornification, the epidermis forms a skin barrier. Alternatively, a disturbed epidermis is unable to carry out the cornification process.
This disturbed barrier may allow the entry of substances into the skin, causing an immunological reaction. Skin inflammation starts at this point and can spread to other organs. The difference in normal skin and skin with immuno-compromised diseases such as psoriasis and dermatitis is very different.
Therefore, the cytokines present in compromised skin influence differentiation and cornification. When the skin is inflamed, the cells start the process of epithelialization by re-establishing the intact keratinocyte layer.
Here, the epidermal stem cells regulate the multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines or growth factors. Another benefit of cytokine is boosting anti-cancer activity by sending signals. These signals may help make abnormal cells die, and normal cells live longer. One specific type of cytokine is called a chemokine.
The science behind Photobiomodulation Controlling Keratinocytes Inflammatory Response
In a recent study, primary human keratinocytes (KCs) were stimulated with 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB). This made the cells mimic pro-inflammatory stress. These cells were illuminated with two wavelengths: 660 nm or 520 nm.
The light wavelengths were able to significantly reduce the mRNA expression of the DNCB-triggered TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 cytokines in KCs. In addition, they enhanced Nrf2 pathway activation. Nrf2 is a crucial factor in regulating skin inflammation.

Nrf2 induced from photobiomodulation creates an inflammatory response in KCs. Furthermore, this mechanism helps in the immunoregulation effect of PBM in inflamed human skin explants. These explants were subjected to 660 nm light.
As a result of this, Langerhans cells migrated into the dermis, preserving their health, and decreased pro-inflammatory cytokine production compared to the DNCB-treated group.
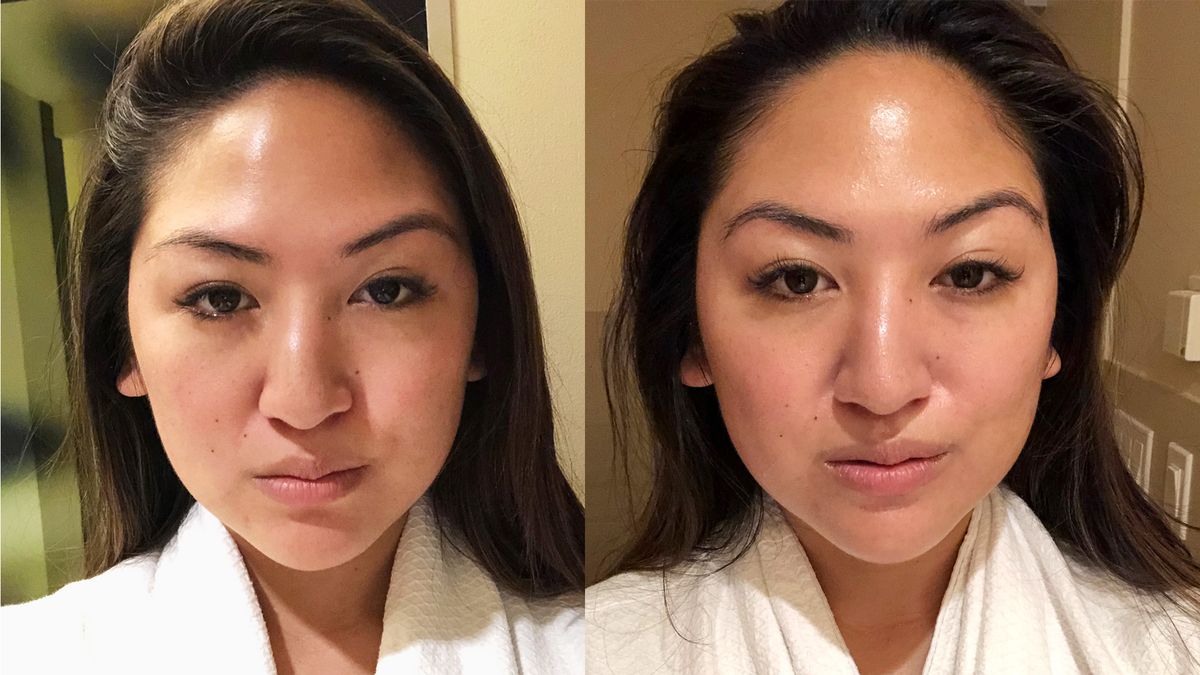
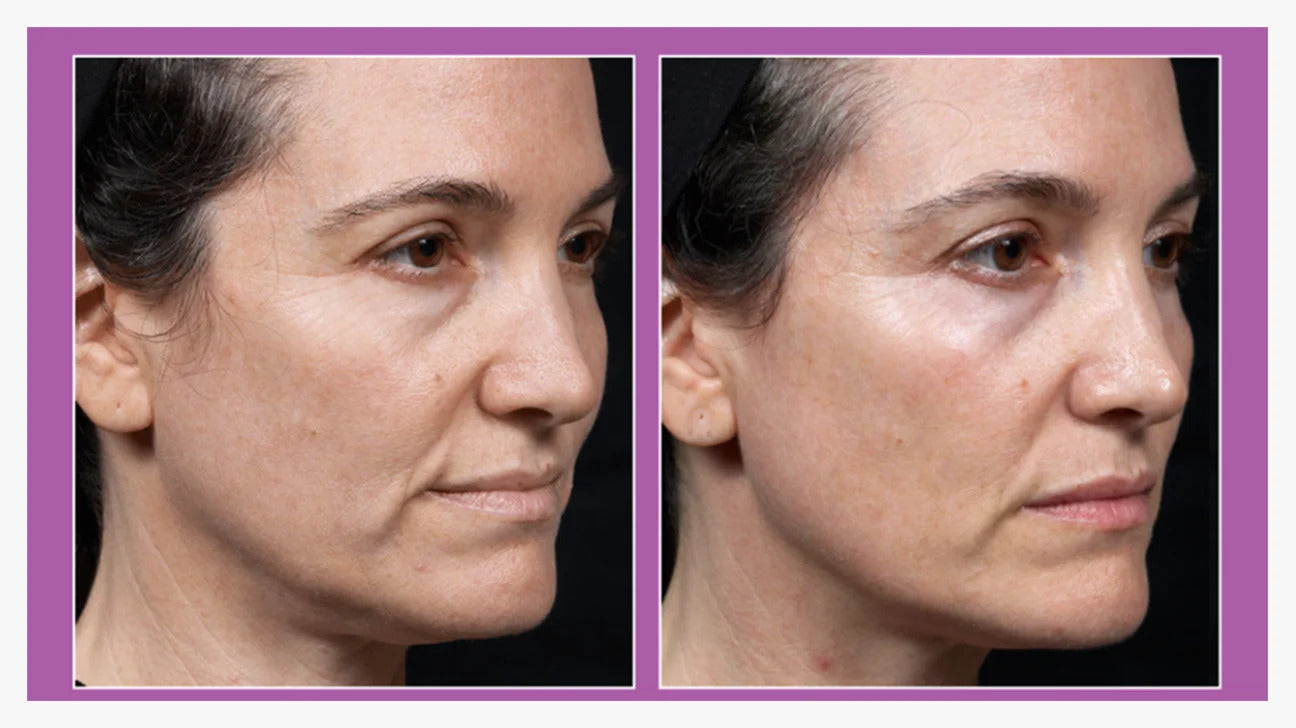
Using Red Light Therapy For Healing Skin Inflammation
Over the years, non-invasive skin healing therapies are gaining popularity. Red light therapy(RLT) is a therapeutic skin technique that uses low-level wavelengths of red light. It is able to penetrate the skin from 1 mm to 2 mm. RLT may have the ability to diminish wrinkles and psoriasis.
Although consistent therapy is needed to see the results. RLT may also be used for scars, acne, edema reduction, and stretch marks. In addition, some people may benefit from repairing muscle tissues and healing chronic pain.
Red light therapy does this by producing a positive biochemical effect in the mitochondria of the cells. This is where the energy of the cell is regenerated to carry out various functions. RLT may help in transporting the electrons, oxygen consumption, and ATP(adenosine triphosphate) levels. This ensures the cell works efficiently when repairing and rejuvenating.
Overall, photobiomodulation using RLT increases blood flow, collagen, and fibroblast activity while reducing inflammation. Fibroblast aids in collagen generation, which further rejuvenates the skin from within.
Choosing an at-home device
Instead of scheduling aesthetician visits, it may be more time-saving to invest in a sturdy red LED face mask. We recommend using the EvenSkyn Mirage Pro LED Phototherapy Face Mask, which is a professional quality photobiomodulation mask.
It has 204 individual units of LEDs that emit red, blue, and yellow lights for facial rejuvenation. The mask comes with built-in eye protection to safeguard them from light. It has an adjustable ergonomic band that fits snugly over the face.

With a remote/power bank, you can control the intensity and color of the light. Red LED is for collagen stimulation and increasing fibroblast activity. Blue light may help in reducing acne-causing bacteria, hence reducing skin inflammation.
The yellow LED is ideal for overall skin rejuvenation and for adding radiance to the surface. If you have wrinkles and fine lines and are looking for an anti-aging solution, the mask emits an efficient 500 Joules of photo-rejuvenating energy per minute in the red light mode.
As discussed earlier, the mask works with continuous use. You may achieve the best results by using the mask for 25 minutes at least thrice a week. In 6-8 weeks, you may notice radiant and less inflamed skin.
Wrapping Up
Now you know how modulating cytokines may help in reducing skin inflammation. Cytokines have a pivotal role in the skin's repair and healing processes. These microscopic messengers help in cell proliferation, tissue repair, and inflammation control.
Understanding skin rejuvenation at the cellular level ensures we develop therapies to support those functions. The potential of Red Light Therapy (RLT) in generating collagen and reducing inflammation is undeniable. By stimulating mitochondria, increasing collagen production, and reducing inflammation, RLT offers a multifaceted approach to enhancing skin health.
Moreover, the convenience and accessibility of at-home RLT devices make it an attractive option for individuals seeking a skincare regimen that aligns with their busy lifestyles. With regular use, these devices may bring about noticeable improvements in skin texture, radiance, and inflammation reduction.
References:
- Avci P, Gupta A, Sadasivam M, Vecchio D, Pam Z, Pam N, Hamblin MR. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) in skin: stimulating, healing, restoring. Semin Cutan Med Surg. March 2013
- Heiskanen V, Hamblin MR. "Photobiomodulation: lasers vs. light emitting diodes?" Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2018 Aug 8
- Gold MH, Andriessen A, Biron J, Andriessen H. "Clinical Efficacy of Self-applied Blue Light Therapy for Mild-to-Moderate Facial Acne." J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009 March
- Opel DR, Hagstrom E, Pace AK, Sisto K, Hirano-Ali SA, Desai S, Swan J. "Light-emitting Diodes: A Brief Review and Clinical Experience." J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015 Jun
- Xu J, Zanvit P, Hu L, Tseng PY, Liu N, Wang F, Liu O, Zhang D, Jin W, Guo N, Han Y, Yin J, Cain A, Hoon MA, Wang S, Chen W. "The Cytokine TGF-β Induces Interleukin-31 Expression from Dermal Dendritic Cells to Activate Sensory Neurons and Stimulate Wound Itching. Immunity." 2020 Aug
- Annapoorna Sreedhar, Leopoldo Aguilera-Aguirre & Keshav K. Singh. "Mitochondria in skin health, aging, and disease." June 2020
- Mehrabani D, Manafi N. "Role of cultured skin fibroblasts in aesthetic and plastic surgery." World J Plast Surg. 2013 Jan
- Sara Salman, Cyprien Guermonprez. "Photobiomodulation Controls Keratinocytes Inflammatory Response through Nrf2 and Reduces Langerhans Cells Activation." January 2023








Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.